It’s been about 30 years since NASA astronauts saved the Hubble space telescope on an immensely daring mission. At the time, it was perhaps the most daring mission scientists had ever conceived. In short, Hubble was launched in 1990 with faulty optics that produced blurry images. Fortunately, however, the space telescope, which orbits Land, was designed to be physically repaired by astronauts. Yes, mid-orbit.
But even with this capability, before Hubble’s launch, no one really expected that those repairs would have to come so soon and so dramatically.
The story begins 14 years earlier, when work was just beginning to “ground” the giant 2.4-meter mirror that would be the center of Hubble’s optical system. By far the largest telescope sent to space At that time, the mirror had to be polished to exact specifications. The contract for this arduous task was awarded to a company called Perkins-Elmer.
Related: NASA wants ideas to boost Hubble Space Telescope to higher orbit with private spacecraft
For three years, technicians worked on the mirror blank. They polished, cleaned and, of course, measured. And they did it again and again. To focus light from distant galaxies, the mirror’s curvature had to be ground to an accuracy of just five microns, or 0.005 millimeters.
Because such precision is beyond the vision of the human eye, technicians used a network of lasers to measure the curvature of the mirror. This grid was maintained by a device called a reflective null checker, which is a fancy name for a metal rod with a cap on the end in which a hole is drilled for a laser to enter and reflect off a bare metal panel.
In 1981, the mirror was complete; Two years later it was combined with the other components of the telescope and prepared for launch aboard a spacecraft. space shuttle in 1986, only for tragedy to strike. He Challenger Disaster What happened in January of that year caused the cessation of space shuttle launches for three years while the accident was investigated. Hubble sat in a clean room, waiting.
Then, on April 24, 1990, his moment finally came when he roared into space aboard the space shuttle discovery to applause at mission control and from astronomers around the world.
However, those cheers quickly turned into tears. Within days, Hubble was active and transmitting images to Earth, but something was wrong. The images were blurry and a chill ran through the place. POT hierarchy. Had $1.5 billion been wasted on a telescope with defective vision?
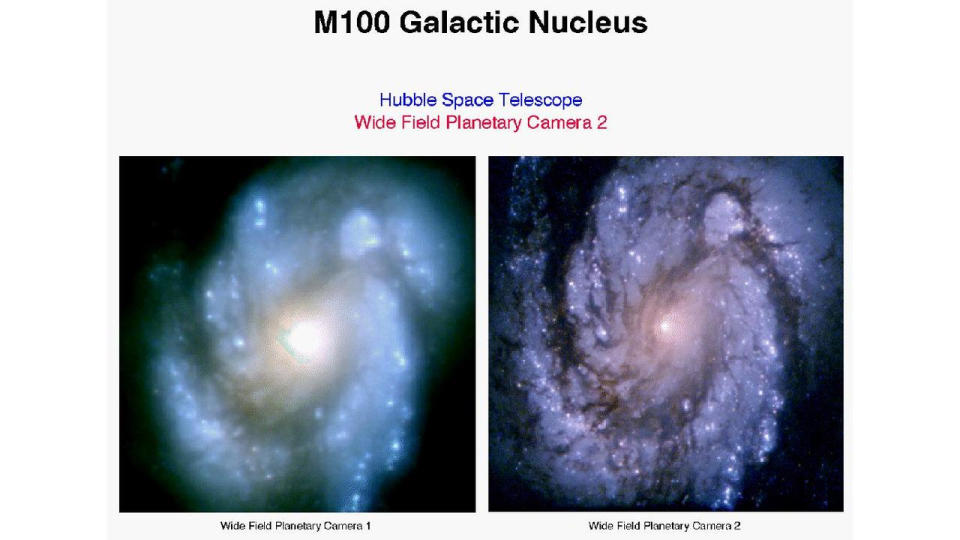
A subsequent investigation discovered what had happened, a catastrophic error that dated back to the grounding of the telescope that had remained hidden all this time. time, like a time bomb. It was found that a flake of paint had come off on one of the reflective null correctors that went unnoticed. This exposed a patch of bare metal where the lasers were reflected instead of what they were intended to reflect. In other words, the reflective null corrector functioned as if it were 1.3 mm out of position.
The consequence of this was that the outer edge of Hubble’s main mirror had been inadvertently polished to the wrong specifications. It became too shallow to deal with this situation by just two microns. Although it may not seem like much, this small mistake had huge repercussions. Hubble was designed to focus at least 70% of incoming light into a small circle, but its faulty mirror meant it could only focus 15% of that light. Everything else was blurry. This distortion is called “spherical aberration.”
When all this came to light, NASA became a public laughing stock, with talk show hosts making jokes at NASA’s expense and politicians demanding answers. In the end, the solution turned out to be surprisingly simple: What else can an optician do for a nearsighted patient besides prescribe glasses?
So that’s what NASA did.
Hubble’s optical system was of the Ritchey-Chrétien design, in which the primary mirror reflects light to a smaller secondary mirror, which on Hubble is only 30 centimeters (12 inches) wide. The secondary mirror reflects light through a hole in the center of the primary mirror, to a focal point behind it where the scientific instruments, i.e. spectrographs and cameras, are located. Fixing Hubble required putting something in the optical path before the light reached focus to correct for spherical aberration. These are the “goggles” and the instrument was called COSTAR, Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement.
Thus, a team of seven brave astronauts: Ken Bowersox, Dick Covey, Kathy Thornton, Jeff Hoffman, Story Musgrave and Tom Akers of NASA, as well as the European Space AgencyClaude Nicollier, trained for months in NASA’s underwater buoyancy tank, practicing the five spacewalks that would be necessary to install COSTAR and replace the original Wide Field and Planetary Camera (WFPC) with a new, more sophisticated model, WFPC 2 They were going to replace the defective gyroscopes with new ones. Space walks were considered some of the most dangerous. space walks tried until then.
On December 2, 1993, the seven astronauts took off on board. space shuttle endeavor on a mission to save Hubble and NASA itself, because if NASA couldn’t repair Hubble, how could it be expected to launch and assemble Hubble? International Space Stationa task that would be much more complex?
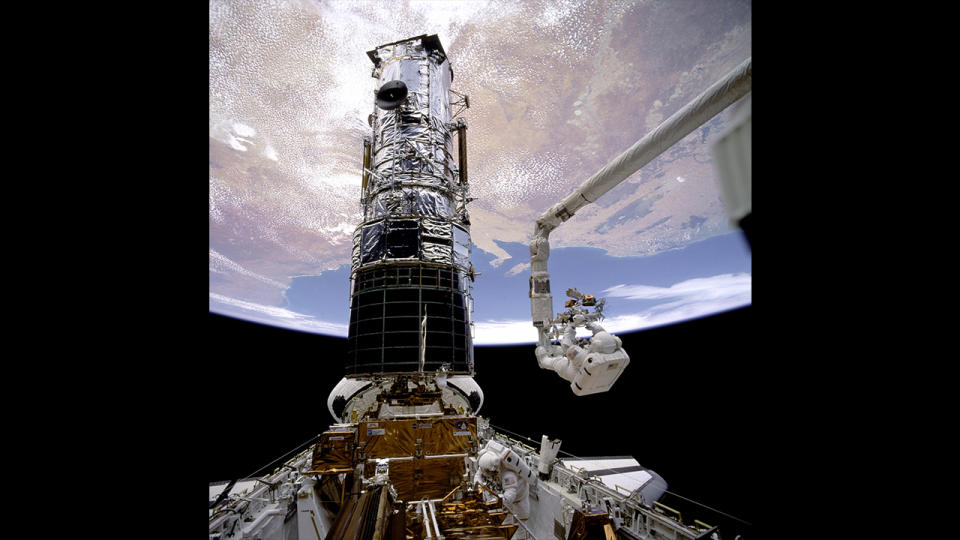


Endeavor grabbed Hubble with its robotic arm, dragging the orbiting observatory into its open cargo bay. The hero astronauts performed all five spacewalks and repairs perfectly, and when Hubble returned images to Earth, they were perfect.
The mission to repair Hubble turned out to be only the first of many telescope maintenance missions over the next 16 years, although none proved as important or dramatic as the first. Ironically, COSTAR wasn’t even needed in the long term: those later maintenance missions replaced the old cameras and spectrographs with new, updated models that were able to correct for spherical aberration on their own. The last maintenance mission, in which the space telescope received a major upgrade, took place in 2009, before the space shuttle fleet was retired.
Related stories:
— The best Hubble Space Telescope photographs of all time.
— Saving Hubble: Astronauts remember first space telescope repair mission 20 years ago
— Hubble FAQ: Inside the Space Telescope’s Latest Repair Mission
While the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) may have stolen much of the spotlight from Hubble, the veteran space observatory is still making vital discoveries. In the last 12 months alone, Hubble has observed changing weather and seasons in Jupiter and Uranusfound that the material falling from SaturnThe rings are warming the planet’s atmospherelook a double quasar since when the universe was only 3 billion years old and has measured the size of the closest known transiting object exoplanet be 1.07 times the diameter of the Earth.
None of the above would have been possible without that brave mission to save the damaged telescope. The repair mission rescued NASA’s reputation, but also secured Hubble’s legacy for the next 30 years, a legacy that has been both profound and astonishing.